The SBI PO 2023 recruitment notification has not been released yet and thus we do not know the number of vacancies for this year. However, if we compare the vacancies from past year then a total of 1673 vacancies were released, so this year also we can expect a number close to this. As far as final selection of SBI PO is concerned the candidates will have to clear all the three stages including prelims, mains, and interview. Many aspirants start preparing early for the exam without waiting for the actual notification which is a good sign of clearing the exam in the first attempt. But, many remain confused as far as previous year papers are concerned. To solve this problem, we have come up with SBI PO Previous Year Paper with Solutions- Download Free PDF. This is a comprehensive PDF with complete questions along with detailed answers and solutions. So, here we are guiding all candidates those who actually want to practice SBI PO previous year paper.
SBI PO Previous Year Paper with Solutions- Download Free PDF
The exam dates for SBI PO 2023 will be released along with the official notification, but the aspirants right now must be aware of the types of questions asked in the SBI PO examination which is why we have SBI PO previous year questions with answers and detailed solutions for you. Candidates those who have already started reparing for SBI PO 2023 must not miss out o this previous year paper as this will definitely help in enhancing your speed and accuracy and will ultimately strengthen your SBI PO exam preparation. Below mentioend are the questions, in order to view the detailed answers and solutions, download the complete SBI PO previous year paper PDF.
SBI PO Previous Year Paper with Solutions – Download Now
SBI PO Previous Year Question Paper
SBI PO Previous Year Questions – Quantitative Aptitude
Directions: Answer the questions based on the information given below.
There are total 6400 books in a college library which started issuing books in the last week of November, out of which, 2400 books were issued to the students in the last week of November and 40% of the remaining books are issued in the following week on Monday. The pie chart given below shows the percentage distribution of the number of books issued on Tuesday to different types of students (1st year, 2nd year, 3rd year, 4th year and 5th year) of the college.
Note: Number of books issued to 2nd year students is 30 more than the number of books issued to 1st year students on Tuesday.
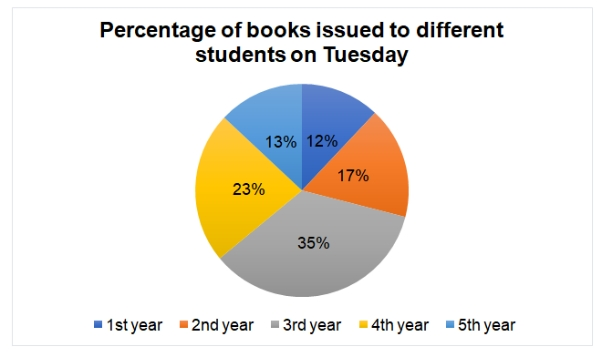
Question 1: If the number of books issued to 3rd year student on Monday is 50% more than the number of books issued to 3rd year student on Tuesday, find the number of books issued to 3rd year student on Monday.
A) 315
B) 325
C) 295
D) 335
E) None of these
SBI PO Prelims 2023 Free Mock Test
Question 2: The number of books issued to 5th year students on Tuesday is what percentage of the number of books issued to 4th year students on the same day?
A) 52.4%
B) 56.5%
C) 61.3%
D) 65.9%
E) 49.1%
Question 3: Find the total number of books issued till Tuesday starting from the last week of November.
A) 4200
B) 4400
C) 4600
D) 4800
E) None of these
Question 4: 20% of the books issued till Tuesday was deposited on Wednesday, and 720 books were issued on Wednesday. Find the number of books left in the library on Wednesday at the end of the day.
A) 2000
B) 1900
C) 1800
D) 2100
E) None of these
Question 5: If each student of 5th year was issued 3 books on Tuesday, then find the number of 5th year students who were issued books on Tuesday.
A) 26
B) 28
C) 32
D) 36
E) None of these
Question 6: What approximate value will come in place of the question mark (?) in the following question? (Note: You are not expected to calculate the exact value.)
782.851/2 + 37.505% of 2688.04 + 48.12 × 34.25 ÷ (67.78) = ?
A) 780
B) 1340
C) 2160
D) 1060
E) 1680
Question 7: What approximate value will come in place of the question mark (?) in the following question? (Note: You are not expected to calculate the exact value.)
116.89 + 286.03 + 128.89 – 50% of 960.09 = 64.89% of ?
A) 420
B) 680
C) 240
D) 580
E) 80
Question 8: What approximate value will come in place of the question mark (?) in the following question?(Note: You are not expected to calculate the exact value.)
{1244.9547 + 3.03 × 1086.98 – (320.97 × 11.0543)} = ?
A) 423
B) 298
C) 516
D) 975
E) 284
Question 9: What approximate value will come in place of the question mark (?) in the following question?(Note: You are not expected to calculate the exact value.)
(75.04% of 839.95 – 15.92 × 15.13) = ? × 26.09
A) 95
B) 15
C) 135
D) 65
E) 185
Question 10: What approximate value will come in place of the question mark (?) in the following question? (Note: You are not expected to calculate the exact value.)
62.45% of 3200.09 + 40.12% of ? = 2095.94
A) 240
B) 120
C) 380
D) 20
E) 520
Question 11: What approximate value will come in place of the question mark (?) in the following question? (Note: You are not expected to calculate the exact value.)
265.08 + (79.98% of 750.08) ÷ 15.12 + ? = 428.09
A) 43
B) 123
C) 246`
D) 372
E) 423
Question 12: Mixture ‘A’ contains 80% acetone and rest 32 litres water. Mixture ‘B’ contains 72 litres acetone and rest 55% water. When two mixtures are mixed, then find the ratio of acetone to water in the resultant mixture.
A) 2:1
B) 6:5
C) 5:3
D) 3:2
E) 4:3
Question 13: Ravish takes 32 days to complete a work while Arnab can complete the same work in 12 days less than Ravish. If Varun can complete 25% of the work in 12 days, then find the time taken by Ravish, Arnab and Varun together to complete 61.25% of the work.
A) 9 days
B) 4 days
C) 8 days
D) 12 days
E) 6 days
Question 14: Two dice were tossed simultaneously. Find the probability that the sum of the numbers obtained on the two dice is a prime number.
A) 5/12
B) 3/8
C) 4/9
D) 1/8
E) 2/9
Question 15: A dog takes 5 leaps for every 4 leap of a frog. If 1 leap of dog is equal to 2 leaps of the frog, then find the ratio of the speed of the dog to that of the frog.
A) 7:5
B) 9:4
C) 3:1
D) 5:2
E) 7:2
Question 16: Anderson is cycling at an average speed of 12 km/hr such that he can reach a certain point at 12 noon. If he cycles at 20 km/hr, then he will reach the destination at 10 a.m. At what speed he should cycle to reach the destination at 11 a.m.
A) 15 km/hr
B) 12.5 km/hr
C) 16.5 km/hr
D) 16 km/hr
E) 14 km/hr
Question 17: The curved surface area of a cylinder whose radius of base and height are in the ratio 5:2, respectively, is 3080 cm2. If the circumference of the base of a cone is 132 cm less than that of the cylinder, then find the radius of the base of the cone.
A) 7 cm
B) 21 cm
C) 35 cm
D) 28 cm
E) 14 cm
Question 18: The percentage profit earned by selling an article ‘A’ for Rs. 2800 is equal to the loss percent incurred by the selling the same article for Rs. 2200. Find the selling price when another article ‘B’ whose cost price is Rs. 700 more than that of article ‘A’ is sold at 15% profit.
A) Rs. 3680
B) Rs. 3240
C) Rs. 3560
D) Rs. 3450
E) Rs. 3220
Question 19: When 12 years is subtracted from the present age of Vipul and the obtained result is divided by 3, then the present age of his nephew is obtained. If the present age of his nephew is 4 years less than the present age of Vipul’s son who is 16 years old, then find the present age of Vipul.
A) 36 years
B) 54 years
C) 48 years
D) 33 years
E) 51 years
SBI PO Previous Year Paper with Solutions – Download PDF Now
Question 20: If the sum of the 1st 21 terms of an AP is equal to the sum of 1st 31 terms of that AP, then find the sum of the 1st 52 terms of the same AP.
A) 0
B) -212
C) -325
D) 212
E) Can’t be determined
Question 21: Suman sold an article at 40% profit. If the profit percentage had been numerically equal to CP, then the profit earned had been 250% more. Find the amount for which Suman sold the article originally.
A) Rs. 164
B) Rs. 208
C) Rs. 196
D) Rs. 224
E) None of these
Question 22: 240 metre long train ‘A’ is running with a speed of 72 km/hr. Train ‘B’ which is 360 metre long is running with a speed of 108 km/h in opposite direction of train ‘A’. For how much time, the smaller train is completely obscured by the larger train?
A) 2.4 seconds
B) 5.6 seconds
C) 3.2 seconds
D) 1.8 seconds
E) None of these
Question 23: There are total 300 students in three sections A, B and C of a class. The average marks of students all three sections were 90.7. The average marks of students of section B and C was 92.5 and the average marks of students of section A was 88. Ratio of number of students in section B and C is 5:4, respectively. Find number of students in section B.
A) 80
B) 100
C) 120
D) 60
E) None of these
SBI PO Prelims 2023 Free Mock Test
Question 24: A train can cross 148 metres long platform in 20.5 seconds while a 192.8 metres long tunnel in 23.3 seconds. Find the time taken by the train to cross a man who is coming towards it at a rate of 28.8 km/h
A) 7.5 seconds
B) 6.5 seconds
C) 9.5 seconds
D) 8.5 seconds
E) 12.5 seconds
Question 25: The following numbers form a series. Find the odd one out.
114, 138, 98, 154, 82, 172
A) 138
B) 98
C) 82
D) 114
E) 172
Question 26: The following numbers form a series. Find the odd one out.
8, 19, 61, 249, 1251, 7517
A) 19
B) 7517
C) 249
D) 1251
E) 61
Question 27: The following numbers form a series. Find the odd one out.
13, 30, 128, 147, 588, 607
A) 30
B) 607
C) 128
D) 147
E) 588
Question 28: The following numbers form a series. Find the odd one out.
228, 307, 188, 357, 132, 421
A) 421
B) 132
C) 188
D) 357
E) 307
Question 29: The following numbers form a series. Find the odd one out.
13, 21, 32, 46, 63, 85
A) 21
B) 85
C) 46
D) 63
E) 32
Question 30: The following numbers form a series. Find the odd one out.
132, 148, 196, 276, 378, 532
A) 276
B) 532
C) 378
D) 148
E) 196
Direction: Answer the questions based on the information given below.
A shopkeeper sold two types of shawls i.e. Pashmina and Knit on different days of a week. The table given below shows the total number of shawls sold, and ratio of number of Pashmina to Knit shawls sold by the shopkeeper.
| Days | Total number of shawls sold | Ratio of number of Pashmina to Knit shawls sold |
| Monday | 1200 | 8:7 |
| Tuesday | 1440 | 7:5 |
| Thursday | 1080 | 5:4 |
| Wednesday | 1280 | 9:7 |
| Friday | 1620 | 4:5 |
Question 31: What is the ratio of number of Pashmina shawls sold on Monday to number of Knit shawls sold on Thursday?
A) 2:3
B) 4:3
C) 3:1
D) 5:4
E) None of these
Question 32: What is the average of number of shawls sold by the shopkeeper on the given days except Thursday?
A) 1395
B) 1375
C) 1385
D) 1345
E) None of these
Question 33: Number of Pashmina shawls sold on Tuesday is how much percent more/less than the number of Knit shawls sold on Wednesday?
A) 70%
B) 50%
C) 75%
D) 60%
E) None of these
Question 34: What is the difference between number of Pashmina shawls sold on Thursday, and number Knit shawls sold on Friday?
A) 280
B) 320
C) 300
D) 400
E) None of these
Question 35: Number of Pashmina and Knit shawls sold on Saturday is 25% more and 20% more, respectively than the same sold on Friday and Tuesday. Total number of shawls sold on Saturday is:
A) 1600
B) 1640
C) 1480
D) 1520
E) None of these
SBI PO Previous Year Paper with Solutions – Download PDF Now
SBI PO Previous Year Questions – English
Question 1: In the following question, one part of the sentence may have an error. Find out which part of the sentence has an error and select the appropriate option. If the sentence is free from error, select ‘No Error’.
A) North Korea, which also has
B) dozens of nuclear weapons,
C) signed that treaty in 1985
D) but withdraws in 2003.
E) No error
Question 2: In the following question, one part of the sentence may have an error. Find out which part of the sentence has an error and select the appropriate option. If the sentence is free from error, select ‘No Error’.
A) Both Russia and the U.S. have thousands
B) of nuclear weapons, most of which are five or more times
C) more powerful than the atomic bombs
D) that leveled Hiroshima and Nagasaki in 1945.
E) No error
Question 3: In the following question, one part of the sentence may have an error. Find out which part of the sentence has an error and select the appropriate option. If the sentence is free from error, select ‘No Error’.
A) Labour migration is always
B) accompany by a dichotomy
C) between economic benefits
D) and social consequences.
E) No error
Question 4: In the following question, one part of the sentence may have an error. Find out which part of the sentence has an error and select the appropriate option. If the sentence is free from error, select ‘No Error’.
A) Despite the negative
B) public attitude to women’s labour
C) migration, it helps much women
D) to gain financial independence.
E) No error
Question 5: In the following question, one part of the sentence may have an error. Find out which part of the sentence has an error and select the appropriate option. If the sentence is free from error, select ‘No Error’.
A) With this decision, nine judges
B) made it possible for the country
C) to institutionalize peace after
D) 50 years of internally conflict.
E) No error
Question 6: In the following question, a sentence is given with three words highlighted in bold. From the options, choose the one that provides the correct arrangement of words in the sentence.
The Supreme Court said that the farmers have a constitutional right to (A) continue with their protests as long as their (B) descend did not (C) dissent into violence.
A) ACB
B) BCA
C) BAC
D) CBA
E) None of the above
Question 7: In the following question, a sentence is given with three words highlighted in bold. From the options, choose the one that provides the correct arrangement of words in the sentence.
Whether one is a driver or a passenger, the (A) maddening Indian road experience is (B) typical and (C) exhausting, and bad for both mental and physical health.
A) ACB
B) CAB
C) BAC
D) CBA
E) None of the above
Question 8: In the following question, a sentence is given with three words highlighted in bold. From the options, choose the one that provides the correct arrangement of words in the sentence.
There are many (A) manpower where India has an advantage because of relatively lower costs of all (B) forms of (C) industries – whether it is professional or factory labour.
A) ACB
B) BCA
C) BAC
D) CBA
E) None of the above
SBI PO Prelims 2023 Free Mock Test
Question 9: In the given question, a word has been given and there are three ways in which the word has been used, in similar or different forms. You need to see which of the sentences have correctly used the highlighted word, and mark that as your answer.
Drive
1. The earth’s dwindling koala numbers cannot be attributed to a single driving factor.
2. Said to possess exceptional drive and extreme intelligence, Norton’s ambitions were not satisfied with the success.
3. When you drive into the city, you see clothes hanging out of virtually every window in the dorms.
A) Only 3
B) Only 1 and 2
C) Only 1 and 3
D) Only 2 and 3
E) All 1, 2 and 3
Question 10: In the given question, a word has been given and there are three ways in which the word has been used, in similar or different forms. You need to see which of the sentences have correctly used the highlighted word, and mark that as your answer.
Order
1. Nelson acted to put an end to the bloodshed, using his ships and men to restore order in the city.
2. International free trade improved the country and in order for Americans to prosper from a strong economy they had no choice but to embrace it.
3. During the battle, Wellesley led his men against the enemy and gave the order to fire.
A) Only 3
B) Only 1 and 2
C) Only 1 and 3
D) Only 2 and 3
E) All 1, 2 and 3
Question 11: In the given question, a word has been given and there are three ways in which the word has been used, in similar or different forms. You need to see which of the sentences have correctly used the highlighted word, and mark that as your answer.
Tend
1. The teachers at this school tend to force-feed their students information, rather than encourage critical thinking and debate.
2. This was considered a custom of the time, and was quite common for households to take in wounded soldiers and tend to them.
3. Very little money will be left over for farmers who tend to apply for the schemes this year.
A) Only 1
B) Only 1 and 2
C) Only 1 and 3
D) Only 2 and 3
E) All 1, 2 and 3
Question 12: In the given question, a word has been given and there are three ways in which the word has been used, in similar or different forms. You need to see which of the sentences have correctly used the highlighted word, and mark that as your answer.
Settle
1. The dentist told Shubham to settle back in the chair.
2. The pudding offers consumers a settle vanilla taste combined with a smooth texture.
3. While the company’s decision may settle one problem, it appears that it may have created a host of others.
A) Only 1 and 2
B) Only 1 and 3
C) Only 1
D) Only 2 and 3
E) All 1, 2 and 3
Question 13: In the following question, a sentence is given with a phrase or idiom highlighted in bold. Select the option given below that can replace the highlighted phrase and mark that as your answer.
At fishing shards of a bacterial DNA from the teeth of bodies in a cemetery, researchers found the starting point of the plague that devastated Eurasia.
A) At verifying
B) At hunting
C) In looking after
D) On investigating
E) No improvement
Question 14: In the following question, a sentence is given with a phrase or idiom highlighted in bold. Select the option given below that can replace the highlighted phrase and mark that as your answer.
When the remaining miles are loomed large, the Gratitude Mile mindset tweak can motivate us to finish strong.
A) has brewed
B) are intimidating
C) are materialised
D) are hovering
E) No improvement
Question 15: In the following question, a sentence is given with a phrase or idiom highlighted in bold. Select the option given below that can replace the highlighted phrase and mark that as your answer.
A powerful tremor in Afghanistan has killed more than 1000 people and the death toll is likely to escalating manifold.
A) to be inflating
B) to be soar
C) to shoot up
D) to enlarging
E) No improvement
Question 16: In the following question, a sentence is given with a phrase or idiom highlighted in bold. Select the option given below that can replace the highlighted phrase and mark that as your answer.
In the quest for self-improvement, it’s tempting to hope on the latest wellness fad.
A) in diving
B) to jump on
C) to plunge
D) in mounting
E) No improvement
Directions: In the following passage, some of the words have been left out and replaced by a blank represented by a letter. First read the passage and try to understand what it is about. Then fill in the blanks as per the questions given.
While large-scale infrastructure development is presented as a ___(A)___ for economic development and reducing poverty in developing countries, such projects pose ___(B)___ risks for local communities living along the river – and for the environment at large. If built, the Salween dams will not only alter the river’s ecosystems and their monsoonal water-level fluctuations, but also transform a wide range of agricultural landscapes that local communities ___(C)___ on for their livelihoods. In recent years, ___(D)___ concerns over hydro-electric projects, international financial entities, such as the International Finance Corporation (IFC), have started to focus on ___(E)___ the idea of sustainable hydropower.
Question 17: (A)
A) summit
B) yield
C) means
D) dearth
E) boon
Question 18: (B)
A) inane
B) informed
C) fragile
D) considerable
E) keen
Question 19: (C)
A) depend
B) commend
C) announce
D) detach
E) repeal
SBI PO Previous Year Paper with Solutions – Download PDF Now
Question 20: (D)
A) against
B) amid
C) towards
D) along
E) for
Question 21: (E)
A) aligning
B) reviving
C) offending
D) hoarding
E) promoting
Directions: Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions that follow.
It is fairly easy to identify an urban area when we see one; however, it is far more complex to determine what an urban area is. Is urban a characteristic of a place or its people? Is it only based on factors like the population size, land surface, primary occupation and the level of development? Does the “urban” area have a culture of its own?
While an urban area is a function of all these metrics, the definitional ambiguity remains a complex task. It is not only necessary to define “urban” in order to understand urbanisation but also to understand the rural-urban divide. This is all the more important in the context of in situ urbanisation, where non-agricultural opportunities are promoted in rural areas, and economic linkages are strengthened. With almost 55 per cent of the population living in cities now and nearly 70 per cent projected to be living in cities by 2050, the attention toward understanding urban settings has never been more glaring. Accompanied with population growth, demographic transition and technological advances, the multi-faceted setting that make up cities have acquired deep academic interests. The rapid rise of cities in developed economies dates back to 200 years, although it is much more recent in developing economies. Searching for a precise definition of “urban” also emphasises the lack of a dichotomy between rural and urban regions. The lines between rural and urban spaces are not as clear as one might think, thereby urging for a definition. For instance, a rural area would have been classified as urban if the streets were laid out in a grid. Such clear transitions are hard to find today. Besides, living in rural areas does not mean exclusion from urban life. The processes of integrative development have meant that rural and urban areas have become more a part of a continuum than a dichotomy. Among the Scandinavian countries, rural and urban spaces are classified on the basis of each other. For example, population density and distance from urban centres are seen as the criteria to define rural areas. In Denmark, which has close to 88 per cent of the population living in cities, there are three classes of rural areas with distinctions between urban-adjacent, intermediate and remote rural areas and a further classification system that compiles the socio-economic profiles of its municipalities.
The Census of 2011 revealed a decline in India’s rural population for the first time. Cities like Bengaluru that have emerged as innovation hubs have grown between 2001 and 2011, subsuming many non-urban areas. This is only expected to grow with the next Census. According to the census definition, a habitation is classified as urban if it has a population of at least 5,000 people, at least 75 per cent of the male working population is employed in non-agricultural pursuits, and the population density is at least 400 people per square kilometre. These are also called Census Towns. The 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendments also enshrine the categorisation of areas into district, intermediate level, and village, as well as the creation of municipalities. The demographic and other criteria determining which sort of municipality is formed vary greatly from state to state. As a result, it is up to the state legislatures to select which municipality will be formed for each urban area.
The variations in determining what can be classified as cities are as dynamic as cities themselves. An urban area’s distinguishing characteristics are tied to its strategic role in the larger community, its value as a civilising force, and its role in enabling the market. However, this does not limit the potential of urban areas, especially in more developed countries where improved mobility has allowed urban inhabitants to live outside the city. The fact that urban population growth happens outside the continually built-up region is commonly acknowledged in various census definitions. The growth of the functional urban region has meant that only the most geographically isolated locations are outside the impact of a metropolis in the more heavily urbanised advanced economies — for example, the Netherlands and the United Kingdom. This aspect of urbanisation not only produces demographic transitions but also alters the relationship of populations with their environment. Settling in urban spaces triggers an image of cemented buildings towering high in the sky as if they were to pierce it. In contrast, rural life is seen as akin to little houses on a prairie. While this does not hold true anymore, it colours our perception of the “urban”.
Question 22: According to the passage, when can a rural area be classified as an urban area?
A) If it brings urban facilities to traditionally agricultural communities.
B) If it is excluded from urban life.
C) If the population density is low.
D) If the streets were laid out in a grid.
E) It can never be classified as an urban area.
Question 23: According to the passage, which of the following statements is/are correct?
A) There has been a rapid development of cities in developed countries in recent years.
B) There are two classes of rural areas in Denmark.
C) The definition of urban area is ambiguous.
D) Among the Scandinavian countries, rural and urban areas cannot be classified on the basis of each other.
E) Nearly 70 percent of the population live in cities now.
Question 24: Which of the following is a criterion used for determining whether a habitation is a ‘census town’?
A) One which has at least 5000 male population
B) One in which the population density is at least 400 people per square metre
C) One in which at least 75 percent male working population is employed in agricultural pursuits
D) One which has emerged as an innovation hub
E) None of the above
Question 25: The urban area’s distinguishing characteristics are linked to:
A) Its role in enabling the market
B) Its role in improving mobility
C) Its role in creating demographic transitions
D) Its growing population
E) Both (a) and (b)
Question 26: Which of the following is closest in meaning to the word ‘dynamic’ as used in the passage?
A) fluid
B) haggard
C) languid
D) bereft
E) stoic
Question 27: Which of the following is opposite in meaning to the word ‘subsuming’ as used in the passage?
A) embracing
B) comprehending
C) entailing
D) denying
E) comprising
SBI PO Previous Year Paper with Solutions – Download PDF Now
Question 28: In the question below, a sentence is given with four words highlighted in bold. From the options, choose the pair of words that need to be interchanged to make the sentence grammatically and meaningfully correct.
Market forces have so far been moving the help in the right direction, now it’s time government stepped in to sector.
A) moving → help
B) moving → stepped
C) help → sector
D) stepped → sector
E) No interchange required
Question 29: In the question below, a sentence is given with four words highlighted in bold. From the options, choose the pair of words that need to be interchanged to make the sentence grammatically and meaningfully correct.
We are heading into a post-antibiotic era, where common infections could once again be deadly.
A) heading → common
B) era → common
C) era → deadly
D) common → deadly
E) No interchange required
Question 30: In the question below, a sentence is given with four words highlighted in bold. From the options, choose the pair of words that need to be interchanged to make the sentence grammatically and meaningfully correct.
We are failing to forced infections, and patients are treat to stay longer in care facilities to overcome them.
A) failing → forced
B) forced → treat
C) forced → overcome
D) treat → overcome
E) No interchange required
प्रश्न 1: None
A) North Korea, which also has
B) dozens of nuclear weapons,
C) signed that treaty in 1985
D) but withdraws in 2003.
E) No error
प्रश्न 2: None
A) Both Russia and the U.S. have thousands
B) of nuclear weapons, most of which are five or more times
C) more powerful than the atomic bombs
D) that leveled Hiroshima and Nagasaki in 1945.
E) No error
प्रश्न 3: None
A) Labour migration is always
B) accompany by a dichotomy
C) between economic benefits
D) and social consequences.
E) No error
प्रश्न 4: None
A) Despite the negative
B) public attitude to women’s labour
C) migration, it helps much women
D) to gain financial independence.
E) No error
प्रश्न 5: None
A) With this decision, nine judges
B) made it possible for the country
C) to institutionalize peace after
D) 50 years of internally conflict.
E) No error
प्रश्न 6: None
A) ACB
B) BCA
C) BAC
D) CBA
E) None of the above
प्रश्न 7: None
A) ACB
B) CAB
C) BAC
D) CBA
E) None of the above
प्रश्न 8: None
A) ACB
B) BCA
C) BAC
D) CBA
E) None of the above
प्रश्न 9: None
A) Only 3
B) Only 1 and 2
C) Only 1 and 3
D) Only 2 and 3
E) All 1, 2 and 3
प्रश्न 10: None
A) Only 3
B) Only 1 and 2
C) Only 1 and 3
D) Only 2 and 3
E) All 1, 2 and 3
प्रश्न 11: None
A) Only 1
B) Only 1 and 2
C) Only 1 and 3
D) Only 2 and 3
E) All 1, 2 and 3
प्रश्न 12: None
A) Only 1 and 2
B) Only 1 and 3
C) Only 1
D) Only 2 and 3
E) All 1, 2 and 3
प्रश्न 13: None
A) At verifying
B) At hunting
C) In looking after
D) On investigating
E) No improvement
SBI PO Previous Year Paper with Solutions – Download PDF Now
प्रश्न 14: None
A) has brewed
B) are intimidating
C) are materialised
D) are hovering
E) No improvement
प्रश्न 15: None
A) to be inflating
B) to be soar
C) to shoot up
D) to enlarging
E) No improvement
प्रश्न 16: None
A) in diving
B) to jump on
C) to plunge
D) in mounting
E) No improvement
Directions: In the following passage, some of the words have been left out and replaced by a blank represented by a letter. First read the passage and try to understand what it is about. Then fill in the blanks as per the questions given.
While large-scale infrastructure development is presented as a ___(A)___ for economic development and reducing poverty in developing countries, such projects pose ___(B)___ risks for local communities living along the river – and for the environment at large. If built, the Salween dams will not only alter the river’s ecosystems and their monsoonal water-level fluctuations, but also transform a wide range of agricultural landscapes that local communities ___(C)___ on for their livelihoods. In recent years, ___(D)___ concerns over hydro-electric projects, international financial entities, such as the International Finance Corporation (IFC), have started to focus on ___(E)___ the idea of sustainable hydropower.
प्रश्न 17: None
A) summit
B) yield
C) means
D) dearth
E) boon
प्रश्न 18: None
A) inane
B) informed
C) fragile
D) considerable
E) keen
प्रश्न 19: None
A) depend
B) commend
C) announce
D) detach
E) repeal
प्रश्न 20: None
A) against
B) amid
C) towards
D) along
E) for
प्रश्न 21: None
A) aligning
B) reviving
C) offending
D) hoarding
E) promoting
SBI PO Prelims 2023 Free Mock Test
Directions: Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions that follow.
It is fairly easy to identify an urban area when we see one; however, it is far more complex to determine what an urban area is. Is urban a characteristic of a place or its people? Is it only based on factors like the population size, land surface, primary occupation and the level of development? Does the “urban” area have a culture of its own?
While an urban area is a function of all these metrics, the definitional ambiguity remains a complex task. It is not only necessary to define “urban” in order to understand urbanisation but also to understand the rural-urban divide. This is all the more important in the context of in situ urbanisation, where non-agricultural opportunities are promoted in rural areas, and economic linkages are strengthened. With almost 55 per cent of the population living in cities now and nearly 70 per cent projected to be living in cities by 2050, the attention toward understanding urban settings has never been more glaring. Accompanied with population growth, demographic transition and technological advances, the multi-faceted setting that make up cities have acquired deep academic interests. The rapid rise of cities in developed economies dates back to 200 years, although it is much more recent in developing economies. Searching for a precise definition of “urban” also emphasises the lack of a dichotomy between rural and urban regions. The lines between rural and urban spaces are not as clear as one might think, thereby urging for a definition. For instance, a rural area would have been classified as urban if the streets were laid out in a grid. Such clear transitions are hard to find today. Besides, living in rural areas does not mean exclusion from urban life. The processes of integrative development have meant that rural and urban areas have become more a part of a continuum than a dichotomy. Among the Scandinavian countries, rural and urban spaces are classified on the basis of each other. For example, population density and distance from urban centres are seen as the criteria to define rural areas. In Denmark, which has close to 88 per cent of the population living in cities, there are three classes of rural areas with distinctions between urban-adjacent, intermediate and remote rural areas and a further classification system that compiles the socio-economic profiles of its municipalities.
The Census of 2011 revealed a decline in India’s rural population for the first time. Cities like Bengaluru that have emerged as innovation hubs have grown between 2001 and 2011, subsuming many non-urban areas. This is only expected to grow with the next Census. According to the census definition, a habitation is classified as urban if it has a population of at least 5,000 people, at least 75 per cent of the male working population is employed in non-agricultural pursuits, and the population density is at least 400 people per square kilometre. These are also called Census Towns. The 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendments also enshrine the categorisation of areas into district, intermediate level, and village, as well as the creation of municipalities. The demographic and other criteria determining which sort of municipality is formed vary greatly from state to state. As a result, it is up to the state legislatures to select which municipality will be formed for each urban area.
The variations in determining what can be classified as cities are as dynamic as cities themselves. An urban area’s distinguishing characteristics are tied to its strategic role in the larger community, its value as a civilising force, and its role in enabling the market. However, this does not limit the potential of urban areas, especially in more developed countries where improved mobility has allowed urban inhabitants to live outside the city. The fact that urban population growth happens outside the continually built-up region is commonly acknowledged in various census definitions. The growth of the functional urban region has meant that only the most geographically isolated locations are outside the impact of a metropolis in the more heavily urbanised advanced economies — for example, the Netherlands and the United Kingdom. This aspect of urbanisation not only produces demographic transitions but also alters the relationship of populations with their environment. Settling in urban spaces triggers an image of cemented buildings towering high in the sky as if they were to pierce it. In contrast, rural life is seen as akin to little houses on a prairie. While this does not hold true anymore, it colours our perception of the “urban”.
प्रश्न 22: None
A) If it brings urban facilities to traditionally agricultural communities.
B) If it is excluded from urban life.
C) If the population density is low.
D) If the streets were laid out in a grid.
E) It can never be classified as an urban area.
प्रश्न 23: None
A) There has been a rapid development of cities in developed countries in recent years.
B) There are two classes of rural areas in Denmark.
C) The definition of urban area is ambiguous.
D) Among the Scandinavian countries, rural and urban areas cannot be classified on the basis of each other.
E) Nearly 70 percent of the population live in cities now.
SBI PO Previous Year Paper with Solutions – Download PDF Now
प्रश्न 24: None
A) One which has at least 5000 male population
B) One in which the population density is at least 400 people per square metre
C) One in which at least 75 percent male working population is employed in agricultural pursuits
D) One which has emerged as an innovation hub
E) None of the above
प्रश्न 25: None
A) Its role in enabling the market
B) Its role in improving mobility
C) Its role in creating demographic transitions
D) Its growing population
E) Both (a) and (b)
प्रश्न 26: None
A) fluid
B) haggard
C) languid
D) bereft
E) stoic
प्रश्न 27: None
A) embracing
B) comprehending
C) entailing
D) denying
E) comprising
प्रश्न 28: None
A) moving → help
B) moving → stepped
C) help → sector
D) stepped → sector
E) No interchange required
प्रश्न 29: None
A) heading → common
B) era → common
C) era → deadly
D) common → deadly
E) No interchange required
प्रश्न 30: None
A) failing → forced
B) forced → treat
C) forced → overcome
D) treat → overcome
E) No interchange required
SBI PO Previous Year Paper with Solutions – Download PDF Now
SBI PO Previous Year Questions – Reasoning
Directions(1-3): Answer the questions based on the information given below.
There are eight members in a family which consists of three generations and two married couples.
A is the brother-in-law of S, who is married. D is the granddaughter of N, who is a male. K is the father of R, who is the sister of S. B is the brother of A and the only son-in-law of M. M is the maternal grandmother of D.
Common Solution:
Clues:
1. M is the maternal grandmother of D.
2. B is the brother of A and the only son-in-law of M.
3. A is the brother-in-law of S, who is married.
Inference: From clues 1, 2 and 3 we conclude that M is the mother of D’s mother. B is married to S.

Clues:
4. K is the father of R, who is the sister of S.
5. D is the granddaughter of N, who is male.
Inference: From clues 4, 5, 6 and 7 we conclude that N is the paternal grandfather of D.
The family tree is given below:
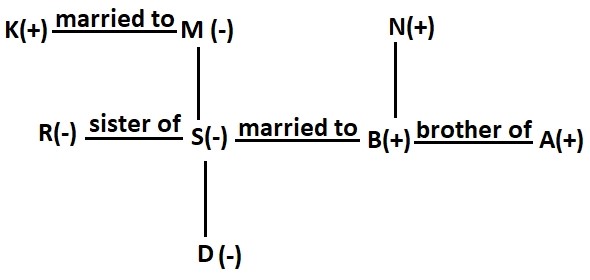
Question 1: How is K related to B?
A) Son
B) Daughter
C) Father-in law
D) Daughter-in-law
E) None of the above
Answer: C)
Solution:
K is the father-in-law of B.
Hence, option c.
Question 2: How is A related to N?
A) Son-in-law
B) Brother
C) Son
D) Nephew
E) Can’t be determined
Answer: C)
Solution:
A is the son of N.
Hence, option c.
Question 3: How is A related to D?
A) Nephew
B) Niece
C) Aunt
D) Uncle
E) Can’t be determined
Answer: D)
Solution:
A is the uncle of D
Hence, option d.
Directions (4-8): Answer the questions based on the information given below.
Eight persons J, K, L, M, N, O, P and Q live on different floors of an eight-floor building such that the bottommost floor is numbered as 1 and the topmost floor is numbered as 8 but not necessarily in the same order. They work in eight different companies viz. HTC, Nike, Adidas, Spice, Dell, Nokia, HP, and Fila. One person works in only one company.
Q lives on an even numbered floor below the 6th floor. O lives three floors above Q. P works in Fila and lives on a floor above O. Three persons live between N and M. K and L works in Nike and Adidas respectively. Three persons live between P and J. N works in HTC and lives on an even numbered floor below P. K lives on one of the floors below L. J does not work in Spice, Dell or HP. Neither Q nor M works in Spice. M lives on an even numbered floor.
Common Solution:
Starting Point: Start with placing Q and O.
Clues:
1. Q lives on an even numbered floor below the 6th floor.
2. O live three floors above Q.
3. P works in Fila and lives on a floor above O.
4. Three persons live between P and J.
Inferences:
From clue 1, Q lives either on 4th or 2nd floor.
From clue 2, O lives either on 7th or 5th floor.
From clue 3, P lives on 8th, 6th, or 7th floor.
From clue 4, P lives on either 7th or 8th floor, J lives either on 3rd or 4th floor, Q lives on 2nd floor.
Case I: P lives on 7th floor.
| Floors | Persons | Company |
| 8 | ||
| 7 | P | Fila |
| 6 | ||
| 5 | O | |
| 4 | ||
| 3 | J | |
| 2 | Q | |
| 1 |
Case II: P lives on 8th floor.
| Floors | Persons | Company |
| 8 | P | Fila |
| 7 | ||
| 6 | ||
| 5 | O | |
| 4 | J | |
| 3 | ||
| 2 | Q | |
| 1 |
Clues:
5. N works in HTC and lives on an even numbered floor below P.
6. Three persons lives between N and M.
7, M lives on an even numbered floor.
8. K lives on one of the floors below L.
Inferences:
From clue 5, clue 6 and clue 7, N lives on 4th floor, Case II is rejected as N and M can’t be placed.
From clue 7 and clue 8, M lives on 8th floor, K lives on 1st floor and L lives on 6th floor.
| Floors | Persons | Company |
| 8 | M | |
| 7 | P | Fila |
| 6 | L | |
| 5 | O | |
| 4 | N | HTC |
| 3 | J | |
| 2 | Q | |
| 1 | K |
Clues:
9. K and L work in Nike and Adidas respectively.
10. J does not work in Spice, Dell or HP.
11. Neither Q nor M works in Spice.
Inferences:
From clue 10, J works in Nokia.
From clue 11, O works in Spice, either Q or M works in HP or Dell.
The final arrangement is as follows:
| Floors | Persons | Company |
| 8 | M | HP/Dell |
| 7 | P | Fila |
| 6 | L | Adidas |
| 5 | O | Spice |
| 4 | N | HTC |
| 3 | J | Nokia |
| 2 | Q | Dell/HP |
| 1 | K | Nike |
Question 4: Which of the following statements is/are definitely correct?
I. M works in Dell
II. Q works in HP
III. J works in Nokia
A) Only Statement I is correct
B) Only Statement II is correct
C) Only Statement III is correct
D) Only Statement I and II is correct
E) All Statements are correct
Answer: C)
Solution:
J works in Nokia is a correct statement.
Hence, option c.
Question 5: Who lives on 6th floor?
A) N
B) K
C) L
D) M
E) None of the above
Answer: C)
Solution:
L lives on 6th floor.
Hence, option c.
Question 6: How many person(s) lives between the one, who works in Nokia and the one, who works in Spice?
A) Three
B) One
C) Two
D) Four
E) None of the above
Answer: B)
Solution:
One person lives between the one, who works in Nokia and the one, who works in Spice
Hence, option b.
Question 7: M works in____.
A) Dell
B) HP
C) Nokia
D) Either (a) or (b)
E) Either (b) or (c)
Answer: D)
Solution:
M works in either Dell or HP.
Hence, option d.
Question 8: Person, who lives on 1st floor, works in_____.
A) Adidas
B) Nike
C) Spice
D) Nokia
E) None of the above
Answer: B)
Solution:
Person, who lives on 1st floor, works in Nike.
Hence, option b.
SBI PO Previous Year Paper with Solutions – Download PDF Now
Question 9: How many such pair(s) of letters are in the word “ATTENDANT” which has as many letters between them (both forward and backward) as in the English alphabetical series?
A) None
B) One
C) Two
D) Three
E) None of the above
Answer: B)
Solution:
Given word:
ATTENDANT
There is one such pairs (NT) which have as many letters between them (both forward and backward) as in the English alphabetical series.
Hence, option b.
Question 10: If we add one to all the digits of the number 2625684775 and then arrange them in ascending order from the left end, then which digit will be 6th from the left end after the rearrangement?
A) 5
B) 7
C) 8
D) 9
E) None of the above
Answer: B)
Solution:
Given number:
2625684775
After adding one to all digits:
3736795886
After rearrangement in ascending order:
3356677889
The 6th digit from the left end after rearrangement is 7.
Hence, option b.
Directions(11-15): Answer the questions based on the information given below.
Seven persons A, B, C, D, E, F and G are sitting in Row 1 facing north whereas S, T, V, W, X, Y, and Z are sitting in Row 2 facing south such that both rows are equidistant and parallel to each other. The persons sitting in Row 1 face the persons siting in Row 2 and vice versa.
D sits 4th to the right of F, who sits 2nd to the left of E. Either F or D sits at one of the extreme ends. W faces E. Y does not sit at any extreme ends of the row. Two persons sits between A and B. C does not face V. X does not face F or D. Two persons sit between W and S. V sits 4th to the right of S, who does not sit adjacent to Z. A faces Y.
Common Solution:
Starting Point: Start with placing D, F, and E.
Clues:
1. D sits 4th to the right of F, who sits 2nd to the left of E.
2. Either F or D sits at one of the extreme ends.
3. W faces E.
4. Two persons sit between W and S.
Inferences:
From clue 1 and clue 2, E sits 3rd from either of the extreme ends of the row.
From clue 3 and clue 4, S sits 3rd to the left or 3rd to the right of W.
Case I: When E sits 3rd from extreme left end of row.
| W | S | |||||
| F | E | D |
Case II: When E sits 3rd from extreme right end of row.
| S | W | |||||
| F | E | D |
Clues:
5. V sits 4th to the right of S, who does not sit adjacent to Z.
6. A faces Y.
7. Y does not sit at any extreme ends of the row.
8. Two persons sit between A and B.
Inferences:
From clue 5, case II is rejected as V can’t be placed. V sits immediate right of W.
From clue 6 and clue 7, A sits immediate left of D.
From clue 8, B sits 2nd to the right of D.
| V | W | Y | S | |||
| F | E | A | D | B |
Clues:
9. C does not face V.
10. X does not face F or D.
Inferences:
From clue 9, C faces S. G faces V.
From clue 10, B faces X.
From clue 4, Z faces F. T faces D.
The final arrangement is as follows:
| Z | V | W | Y | T | S | X |
| F | G | E | A | D | C | B |
Question 11: What is the position of A with respect to B?
A) 2nd to the left
B) 2nd to the right
C) 3rd to the left
D) 3rd to the right
E) None of the above
Answer: C)
Solution:
A sits 3rd to the left of B.
Hence, option c.
Question 12: ____ sits 2nd to the left of Y.
A) Z
B) V
C) X
D) S
E) W
Answer: D)
Solution:
S sits 2nd to the left of Y.
Hence, option d.
Question 13: How many persons sit between Z and the one, who faces D?
A) Three
B) One
C) Two
D) None
E) Cannot be determined
Answer: A)
Solution:
Three persons sit between Z and T, who faces D.
Hence, option a.
Question 14: D sits ____ to the left of C.
A) Immediate
B) Second
C) Fourth
D) Third
E) None of the above
Answer: A)
Solution:
D sits immediate to the left of C.
Hence, option a.
Question 15: Which of the following statement is/are not correct?
A) V sits immediate left of Z
B) X sits immediate left of S
C) E sits 2nd to the left of F
D) E sits immediate right of G
E) None of the above
Answer: C)
Solution:
E sits 2nd to the left of F is an incorrect statement.
Hence, option c.
Question 16: In the question, assuming the given statements to be true, find which of the following conclusion(s) among the three conclusions is/are true and then give your answer accordingly.
Statement:
I≥J≥R=U≥S; T<M<N; L=S≥T
Conclusions:
I. I≥M
II. R≥T
III. J>S
A) Only conclusion III is true.
B) Only conclusion I and II are true.
C) Only conclusion II is true
D) Only conclusion II and III are true.
E) All the conclusions are true
Answer: C)
Solution:
Given:
I≥J≥R=U≥S; T<M<N; L=S≥T
On combining the given statement, we have
I≥J≥R=U≥L=S≥T<M<N
Conclusion:
I. I≥ M: False (As I≥J≥R=U≥L=S≥T<M, so relation between I and M cannot be determined)
II. R≥ T: True (AsR=U≥L=S≥T, so R≥T)
III. J> S: False (As J≥R=U≥L=S, so J≥S)
Only conclusion II is true.
Hence, option c.
SBI PO Prelims 2023 Free Mock Test
Question 17: In the question, assuming the given statements to be true, find which of the following conclusion(s) among the three conclusions is/are true and then give your answer accordingly.
Statement:
J<R<G<L<M; N>T>M;J>K=C
Conclusions:
I. T<C
II. N<G
III. M> R
A) Only conclusion III is true.
B) Only conclusion I and II are true.
C) Only conclusion II is true
D) Only conclusion II and III are true.
E) All the conclusions are true
Answer: A)
Solution:
Given:
J<R<G<L<M; N>T>M;J>K=C
On combining the given statement, we have,
C=K<J<R<G<L<M<T<N
Conclusion:
I. T< C: False (As C=K<J<R<G<L<M<T, so T>C)
II. N < G: False (As G<L<M<T<N, so N>G)
III. M > R: True (As R<G<L<M, so M>R)
Only conclusion III is true.
Hence, option a.
Question 18: In the question, assuming the given statements to be true, find which of the following conclusion(s) among the three conclusions is/are true and then give your answer accordingly.
Statement:
P=R≥O=M, S<E≤O, T<K≤R
Conclusions:
I. P>S
II. T≥O
III. E≤R
A) Only conclusion III is true.
B) Only conclusion I and III are true.
C) Only conclusion II is true
D) Only conclusion II and III are true.
E) All the conclusions are true
Answer: B)
Solution:
Given:
P=R≥O=M, S<E≤O, T<K≤R
On combining the given statement, we have,
T<K≤P=R≥O=M≥E>S
Conclusion:
I. P>S: True (As P=R≥O=M≥E>S, so P>S)
II. T≥O: False (As T<K≤P=R≥O, so relation between T and O cannot be determined)
III. E≤ R: True (As R≥O=M≥E, so, E≤R)
Only conclusion I and III are true.
Hence, option b.
SBI PO Previous Year Paper with Solutions – Download PDF Now
Question 19: Which of the following symbols should be placed in the blank spaces respectively (in the same order from left to right) in order to complete the given expression in such a manner that ‘R≥Y’ definitely holds true?
A _ R _ T _ L _ Y
A) >, <, ≥, =
B) >, >, >, =
C) <, >, ≥, =
D) >, ≥, ≥, =
E) <, >, ≥, ≤
Answer: D)
Solution:
On substituting option in given expression:
Option (a): A > R < T ≥ L = Y: Relation between R and Y can’t be determined.
Option (b): A > R > T > L = Y, so R > Y.
Option (c): A < R > T ≥ L = Y, so R > Y.
Option (d): A > R ≥ T ≥ L = Y, so R ≥ Y
Option (e): A < R > T ≥ L ≤ Y: Relation between R and Y can’t be determined.
Hence, option d.
Directions(20-23): Answer the questions based on the information given below.
Nine persons are posted in the Indian army at different designations. Designations (from senior to junior) are Admiral, General, Brigadier, Lieutenant, Colonel, Major, Captain, Subedar, and Havildar i.e. Admiral is the highest designation and Havildar is the lowest designation.
Only three persons are junior to T. Two designations lie between the designations of O and R, who is senior to O. R is neither Admiral nor colonel. M is senior to Q but junior to U. U is junior to N. U is not designated as a lieutenant. Three designations lie between the designations of S and P, who is junior to T. S is not designated as Colonel.
Common Solution:
Starting Point: First consider the direct statements/clues.
Clue:
1. Only three persons are junior to T.
2. Three persons are designated between S and P, who is junior to T.
3. S is not designated as Colonel.
Inference: From clues 1, 2 and 3 we conclude that there will be two possible ways to arrange S and P.
Case 1: When S was Lieutenant.
| Designation | Person |
| Admiral | |
| General | |
| Brigadier | |
| Lieutenant | S |
| Colonel | |
| Major | T |
| Captain | |
| Subedar | P |
| Havildar |
Case 2: When S was Brigadier.
| Designation | Person |
| Admiral | |
| General | |
| Brigadier | S |
| Lieutenant | |
| Colonel | |
| Major | T |
| Captain | P |
| Subedar | |
| Havildar |
Clue:
4. Two persons are designated between O and R, who was senior to O.
5. R was neither Admiral nor colonel.
Inference:
From clue 4 and clue 5, O is the Colonel. R is the General.
Case 1: When S was Lieutenant.
| Designation | Person |
| Admiral | |
| General | R |
| Brigadier | |
| Lieutenant | S |
| Colonel | O |
| Major | T |
| Captain | |
| Subedar | P |
| Havildar |
Case 2: When S was Brigadier.
| Designation | Person |
| Admiral | |
| General | R |
| Brigadier | S |
| Lieutenant | |
| Colonel | O |
| Major | T |
| Captain | P |
| Subedar | |
| Havildar |
Clues:
6. M is senior to Q but junior to U.
7. U is junior to N.
8. U is not designated as a lieutenant.
Inference: From clues 6, 7 and 8, case 2 is rejected. And thus, N is the Admiral, U is the Brigadier, Q is the havildar.
The final table is given below:
| Designation | Person |
| Admiral | N |
| General | R |
| Brigadier | U |
| Lieutenant | S |
| Colonel | O |
| Major | T |
| Captain | M |
| Subedar | P |
| Havildar | Q |
Question 20: Who among the following is the Admiral?
A) S
B) R
C) U
D) N
E) M
Answer: D)
Solution:
N is the Admiral.
Hence, option d.
SBI PO Prelims 2023 Free Mock Test
Question 21: How many persons are junior to O?
A) Three
B) None
C) Two
D) Five
E) None of the above
Answer: E)
Solution:
Four persons are junior to O.
Hence, option e.
Question 22: What is the designation of P?
A) Subedar
B) Captain
C) Colonel
D) Major
E) None of the above
Answer: A)
Solution:
P is designated as Subedar.
Hence, option a.
Question 23: How many persons are designated between N and Captain?
A) Four
B) Three
C) Five
D) Six
E) None of the above
Answer: C)
Solution:
Five persons are designated between N and Captain.
Hence, option c.
Directions(24-28): Answer the following question based on the information given below.
In a certain code language,
I. ‘some birds fly high’ is written as ‘rop, lup, rts, mus’
II. ‘some fish swim deep’ is written as ‘rop, jhr, bjk, mok ’.
III. ‘birds are high’ is written as ‘vot, rts, lup’.
IV. ‘high and deep’ is written as ‘bjk, lup, das’.
Common Solution:
From statement I, III and IV, ‘high’ is coded as ‘lup’.
From statement I and II, ‘some’ is coded as ‘rop’.
From statement I and III, ‘birds’ is coded as ‘rts’.
From statement I alone, ‘fly’ is coded as ‘mus’.
From statement II and IV, ‘deep’ is coded as ‘bjk’.
From statement III alone, ‘are’ is coded as ‘vot’.
From statement IV alone, ‘and’ is coded as ‘das’.
From statement II, ‘fish’ and ‘swim’ is coded as ‘jhr’ and ‘mok’.
| Word | High | some | birds | fly | deep | and | are | fish | swim |
| Code | lup | rop | rts | mus | bjk | das | vot | mok/jhr | jhr/mok |
Question 24: What is the code for ‘deep’?
A) jhr
B) bjk
C) mok
D) das
E) None of the above
Answer: B)
Solution:
The code for ‘deep’ is ‘bjk’.
Hence, option b.
Question 25: Which of the following is coded as ‘vot’?
A) are
B) bird
C) high
D) deep
E) None of the above
Answer: A)
Solution:
‘are’ is coded as ‘vot’.
Hence, option a.
Question 26: What is the code for ‘fish and high’?
A) mok das lup
B) rts jhr mok
C) mok vot das
D) jhr das lup
E) Cannot be determined
Answer: E)
Solution:
Code for ‘fish and high’ can be ‘mok das lup’ or ‘jhr das lup’.
Hence, option e.
Question 27: ___ is coded as ‘mus’.
A) deep
B) birds
C) fly
D) are
E) None of the above
Answer: C)
Solution:
‘fly’ is coded as ‘mus’.
Hence, option c.
Question 28: Which of the following statement is incorrect?
A) ‘and’ is coded as ‘das’.
B) ‘bjk’ is the code for ‘deep’.
C) ‘some birds’ is coded as ‘rop rts’.
D) ‘some fish’ is coded as ‘mok jhr’
E) All statements are incorrect.
Answer: D)
Solution:
Option (a): Correct (‘and’ is coded as ‘das’.)
Option (b): Correct (‘bjk’ is the code for ‘deep’.)
Option (c): Correct (‘some birds’ is coded as ‘rop rts’.)
Option (d): Incorrect (‘some fish’ is coded as ‘rop mok’ or ‘rop jhr’)
Hence, option d.
Directions(29-33): Answer the questions based on the information given below.
Eight persons (P, Q, R, S, T, U, V and W) were born in eight different years (1984, 1988, 1991, 1993, 1997, 2000, 2003 and 2008) but not necessarily in the same order.
Note: Consider all persons were born on 31st December in given years. Ages of these persons are calculated with respect to 31st December 2021.
S was born in an odd numbered year before Q. T is elder than S but not the eldest. V was born in one of the years before R and in a leap year. The age difference between W and P is 5 years. U was born in a leap year. Q is 10 years elder than W.
Common Solution:
Starting Point: First we calculate age of persons according to their birth year. (37, 33, 30, 28, 24, 21, 18 and 13) (in years) with respect to 31st December 2021. Now we start with definite clues/information.
Clues:
1. The age difference between W and P is 5 years.
2. Q is 10 years elder than W.
Inferences:
From clue 1 and 2, we get W was born in 2003, P was born in 2008, and Q was born in 1993.
| Years | Ages | Persons |
| 1984 | 37 | |
| 1988 | 33 | |
| 1991 | 30 | |
| 1993 | 28 | Q |
| 1997 | 24 | |
| 2000 | 21 | |
| 2003 | 18 | W |
| 2008 | 13 | P |
Clues:
3.S was born in an odd numbered year before Q.
4.T is elder than S but not the eldest.
5. V was born in one of the years before R and in a leap year.
6. U was born in a leap year.
Inferences:
From clue 3, we get S was born in 1991.
From clue 4, we get T was born in 1988.
From clue 5 and 6, V was born in 1984, R was born in 1997 and U was born in 2000.
The final arrangement is as follows:
| Years | Ages | Persons |
| 1984 | 37 | V |
| 1988 | 33 | T |
| 1991 | 30 | S |
| 1993 | 28 | Q |
| 1997 | 24 | R |
| 2000 | 21 | U |
| 2003 | 18 | W |
| 2008 | 13 | P |
Question 29: ___ was born in 1988.
A) W
B) P
C) S
D) T
E) None of the above
Answer: D)
Solution:
T was born in 1988.
Hence, option d.
Question 30: V is ___ elder than S.
A) 5 years
B) 4 years
C) 7 years
D) 3 years
E) None of the above
Answer: C)
Solution:
V is 7 years elder than S.
Hence, option c.
Question 31: How many persons are younger than U?
A) Three
B) One
C) Two
D) Five
E) Four
Answer: C)
Solution:
Two persons are younger than U.
Hence, option c.
Question 32: What is the sum of ages of V and R?
A) 58 years
B) 51 years
C) 61 years
D) 67 years
E) None of the above
Answer: C)
Solution:
The sum of ages of the V and R is (37 + 24) = 61 years.
Hence, option c.
Question 33: P was born in____.
A) 2003
B) 2008
C) 1988
D) 1993
E) None of the above
Answer: B)
Solution:
P was born in 2008.
Hence, option b.
Question 34: In the question below some statements are given followed by two conclusions I and II. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusion definitely follows from the given statements, disregarding commonly known facts.
Statements:
A few Pens are Pencils
No Erasers are Pens
Some Crayons are Erasers
Conclusions:
I. Some Crayons are not Pens
II. At least Some Pencils are not Erasers
A) Neither Conclusion I nor Conclusion II follows
B) Only Conclusion I follows
C) Only Conclusion II follows
D) Both Conclusion I and Conclusion II follow
E) Either Conclusion I or Conclusion II follows
Answer: D)
Solution:
Following figure can be formed:
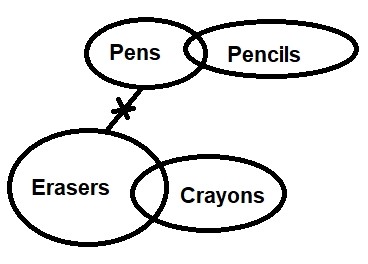
From the figure, both Conclusion I and Conclusion II follow.
Hence, option d.
Question 35: In the question below some statements are given followed by two conclusions Iand II. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusion definitely follows from the given statements, disregarding commonly known facts.
Statements:
No Wells are Taps
Only Taps are Tubewells
Only a few Taps are Pipes
Conclusions:
I. No Pipes are Tubewells
II. Some Wells being Tubewells is a possibility
A) Neither Conclusion I nor Conclusion II follows
B) Only Conclusion II follows
C) Only Conclusion I follows
D) Both Conclusion I and Conclusion II follow
E) Either Conclusion I or Conclusion II follows
Answer: C)
Solution:
Following figure can be formed:
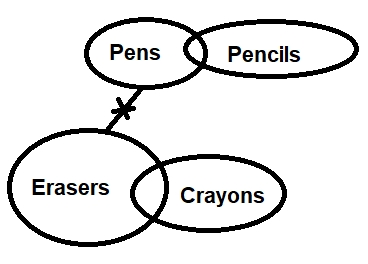
From the figure, only Conclusion I follows.
Hence, option c.
To check detailed answers with solutions, download the complete SBI PO previus year Paper PDF for free.
- Sign Up on Practicemock for Updated Current Affairs, Free Topic Tests and Free Mini Mocks
- Sign Up Here to Download Free Study Material
Free Mock Tests for the Upcoming Exams
- RRB PO 2024 Free Mock Test
- RRB Clerk 2024 Free Mock Test
- SSC MTS Free Mock Test
- SSC CHSL Free Mock Test
- SSC CGL Free Mock Test
- GATE Mechanical Free Mock Test
- GATE Civil Free Mock Test
- NABARD Gr. A Free Mock Test
- SBI Clerk Mains Free Mock Test
- SSC CPO Free Mock Test
- AFCAT Free Mock Test
- CAT Free Mock Test
- NIACL Assistant Free Mock Test
- UIIC AO Free Mock Test
- UIIC Assistant Free Mock Test
- GIC Assistant Manager Free Mock Test
- NICL AO Free Mock Test
- Free SSC Live Test
- UPSC CSAT Free Mock Test
- CDS-I Free Mock Test
- RRB ALP Free Mock Test


